MMeasurement Scales in SPSS
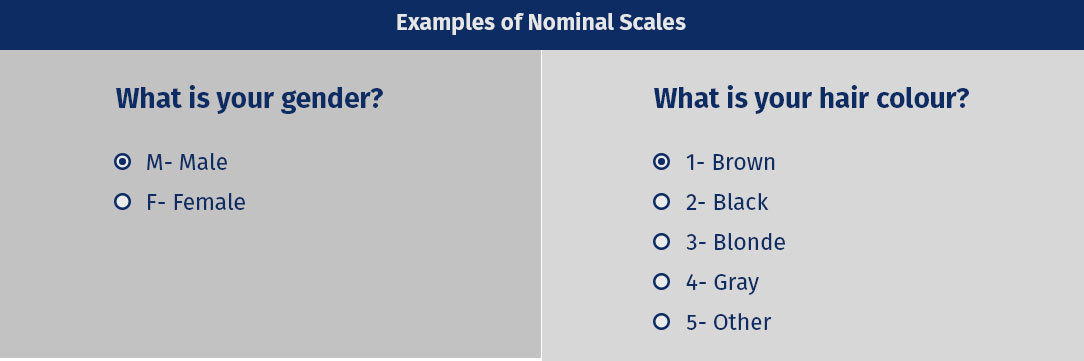
It is measurement scale in which numbers are used as "tags"or "labels" which is used to classify an object.It deals with non-numeric variables.It is used for the purpose of classification. for example, in case of gender scale,it can be classified as Male=1 and Female=2. It is used for only for counting purposes.

2.Ordinal:
It is the second level of measurement in which ranking of data without actually establishing the degree of variation between them.
- Likert Scale through which we can measure the order.

Scale:
Divided into two parts:
1. Interval Scale
2. Ratio Scale
1.Interval Scale:
In this measurement variables are measured in exact manner not in relative manner.
Example:
- Likert Scale
- Net Promoter Score(NPS)
- Bipolar Matrix Table
2.Ratio Scale
It allows researchers to compare the differences or intervals. The ratio scale has a unique feature. It possesses the character of the origin or zero points.
Example:
An example of a ratio scale is:
What is your weight in Kgs?
- Less than 55 kgs
- 55 – 75 kgs
- 76 – 85 kgs
- 86 – 95 kgs



Comments
Post a Comment