MMEAN,MEDIAN AND MODE
In order to summarize your data, you can do this using two methods:
- Graphs.
- Central Tendency methods.
1. Graphs: Using various graphs we can easily summarize our data and get into the result.
2. Central Tendency Method: It represents the center point or typical value of dataset. It represents the data to cluster to a middle value.
Measures of Central Tendency
It can be measured through three different:
1. Mean
2. Median
3. Mode
1. Mean:
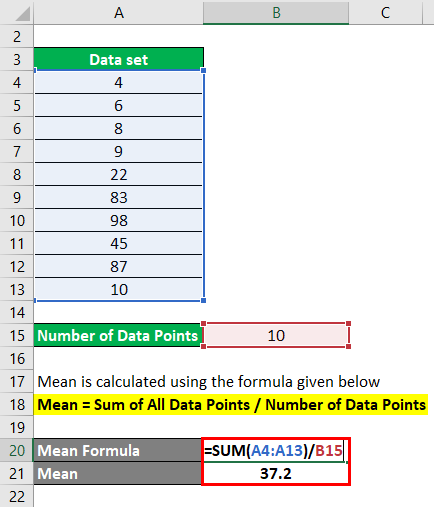
It is one of the common central tendency method used.It can used for discrete and continuous data.It is given by sum of all values of dataset divided by number of values in the dataset. So if we have n values in dataset and they have values like x1,x2,x3,x4 etc.
Mean Formula – Example #1
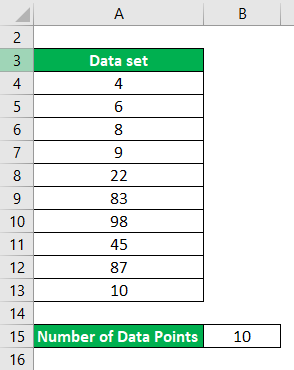
Let say you have a data set with 10 data points and we want to calculate mean for that. Data set : {4,6,8,9,22,83,98,45,87,10}
2. Median:
The median is the middle score for a set of data that has been arranged in order of magnitude.Suppose we have the data below:
| 65 | 55 | 89 | 56 | 35 | 14 | 56 | 55 | 87 | 45 | 92 |
| 14 | 35 | 45 | 55 | 55 | 56 | 56 | 65 | 87 | 89 | 92 |
3. Mode:
Number which is occurring most often in a given set of dataset. for e.g. in {6, 3, 9, 6, 6, 5, 9, 3}
which the mode 6 which occur most. The mode is 6.


Comments
Post a Comment